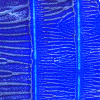
| Decalcomania is fertile ground for experimentation. |
| Procedure |
| Secure a piece of paper to a flat, horizontal surface such as a table top. |
Apply some paint to the surface and place another piece of paper on top of the paint.
| Apply pressure to the top piece of paper, flattening the paint to a thin layer. |
Lift off the top piece of paper and note the branching pattern you observe. |
|
| Exprimental parameters include |
| the viscosity of the paint |
| the stiffness of the paper |
| the speed with which the papers are pulled apart |
| how tightly together the two layers of paper are pressed |
| reprocessing (press together, pull apart, repeat a few times.
What do you see? Repeat many times - does the pattern change?) |
| reprocessing with rotation (press together, pull apart, rotate the top page, repeat.) |
| and on and on - there are many more possibilities |
|
| Quantification These experiments can be quantified in several ways. |
| Count the number of branches off the longer branches. What is the average value, the
range of the values? |
| Calculate the ratio of the lengths of successive branches. What is the average value, the
range of the values? |
| Once scanned, the box-counting dimension procedure can be used to
estimate the dimension fo the longer branches. What is the average value, the
range of the values? |
|
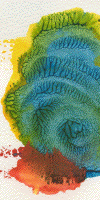
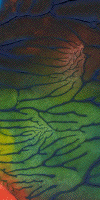
| Here are selections from three recent student projects. |
|
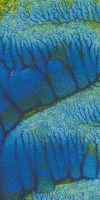
| Finally, here are some additional color examples. Click each picture for a
larger version in a new window. |
|