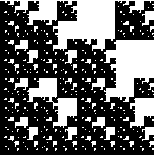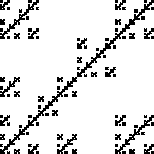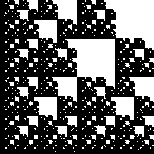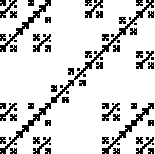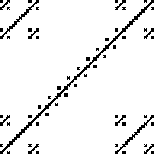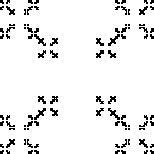| Recall the Moran
equation. For a self-similar fractal made of N copies scaled by r1,
r2, ..., rN, the similarity dimension d is the solution of |
| r1d + r2d + ...
+ rNd = 1 |
| For example, consider the fractal on the left. |
|
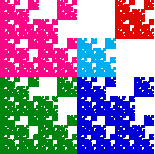
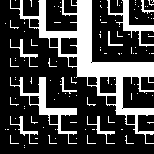
| The decomposition of the right shows this fractal is composed
of three copies scaled by 1/2 and two copies scaled by 1/4.
The Moran equation is |
| 3(1/2)d + 2(1/4)d = 1 |
| Noting 1/4 = (1/2)2, we have |
| 1 = 3(1/2)d + 2((1/2)2)d =
3(1/2)d + 2((1/2)d)2 |
| Writing x = (1/2)d, we see the Moran equation is a quadratic equation |
| 2 x2 + 3 x - 1 = 0 |
| The solution is x = (-3 +/- Sqrt(32 - 4*2*(-1)))/(2*2) =
(-3 +/- Sqrt(17))/4 |
| Because x must be positive, we have x = (-3 + Sqrt(17))/4 and so |
| (1/2)d = (-3 + Sqrt(17))/4 |
| Taking Logs and solving for d, we obtain |
| d = Log((-3 + Sqrt(17))/4)/Log(1/2), approximately 1.83251 |
| Exact solutions can be obtained in this way if all the scaling
factors are powers of the same number. |
Compute the similarity dimensions of these fractals. Click each picture for the solution.