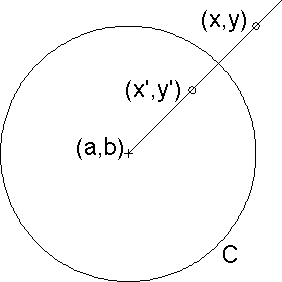Circle Inversion Fractals
Properties of Inversion
Suppose (x,y) lies on the circle C.
Then dist((a,b), (x,y)) = r, the radius of the circle C.
Because dist((a,b), (x,y))*dist((a,b), (x',y')) = r2, we see
dist((a,b), (x',y')) = r
and so (x',y') must lie on C.
Because (x,y) and (x',y') lie on the same ray from
the center of C, we see
(x'y') = (x,y)
That is, inversion across C takes every point of C to itself.
Return to properties of inversion.